Search Results
15 items found for ""
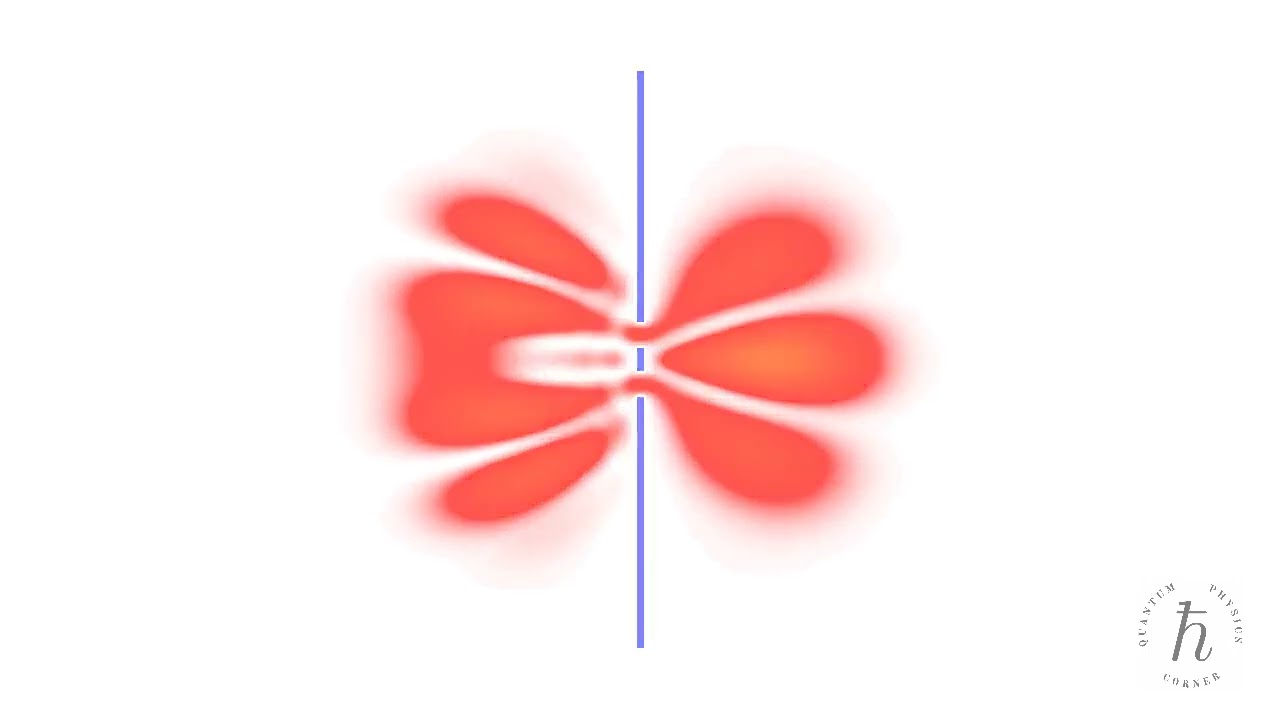
- Double-slit interference
A quantum particle passes through an opaque screen with two slits, resulting in an interference pattern. The time evolution of the probability density is determined by numerically solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation.
- Calculus Refresher: Question 10
Find the following integral. Here are two solutions.
- Calculus Refresher: Question 9
Solve the following differential equation. The equation can be solved as follows.
- Calculus Refresher: Question 8
Find the following integral. Solution:
- Calculus Refresher: Question 7
Solve the following differential equation. The equation can be solved as follows.
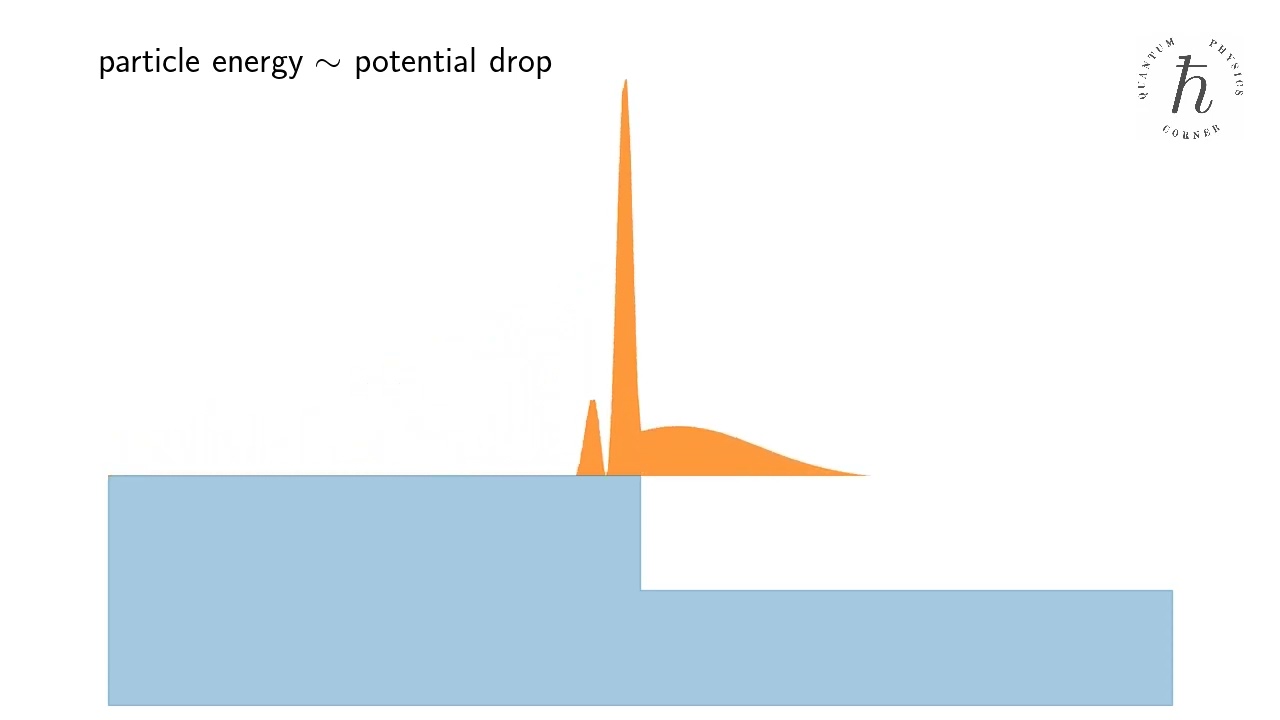
- Quantum reflection
Counterintuitive reflection of a quantum particle from a downward potential step. Wait for it!
- Calculus Refresher: Question 6
Find the following integral. Solution:
- Calculus Refresher: Question 5
Solve the following differential equation. The equation can be solved as follows.
- Calculus Refresher: Question 4
Find the following integral. Here are two solutions.
- Quantum egg
The probability density (i.e. the modulus squared of the wave function) of a non-relativistic quantum particles spreading inside an egg shaped cavity. The equation of the cavity's boundary is r = cos³(φ) + 0.2*cos(φ)*sin²(φ). The time-evolution of the wave function was obtained by solving the time-dependent Schrödinger equation.
- Calculus Refresher: Question 3
Solve the following differential equation. The equation can be solved as follows.